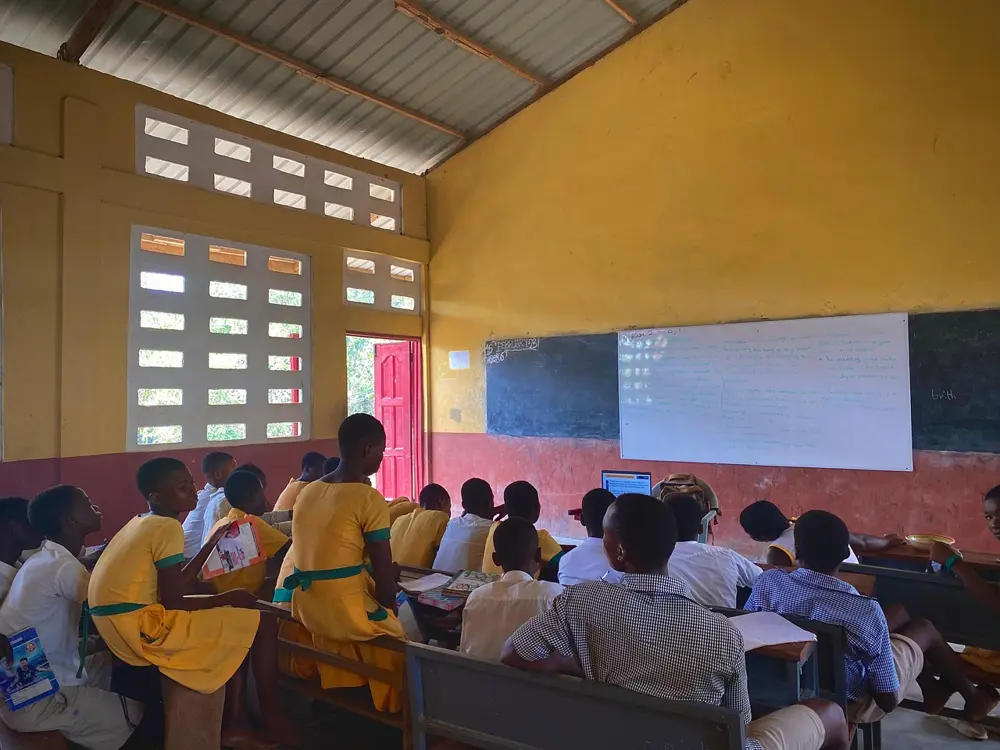
What Are Learning Theories?
Learning theories are ideas that explain how people gain knowledge, skills, or habits. They help teachers understand how students learn and guide how they teach in the classroom.
1. Behaviorism
What is Bevaviorism Theory?
This theory states that learning is a change in behavior caused by the environment. It uses rewards and punishments.
Key Theorists: Ivan Pavlov, John Watson, B.F. Skinner.
Example in Ghana: A teacher gives stars, applause, or praise when students answer correctly. This motivates them to repeat good behavior. Misbehavior may receive a time-out or warning.
Relevance: Helps with classroom discipline and teaching basic facts like alphabets or multiplication tables.
2. Cognitivism
What is Cognitivism Theory?
This theory suggests that learning happens through mental activities like thinking, remembering, and solving problems.
Key Theorists: Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner.
Example in Ghana: Teachers use mind maps, storytelling, charts, or local examples to help students understand and remember. For instance, explaining measurement using farm tools or selling tomatoes in the market.
Relevance: Useful for teaching reading, writing, math, and problem-solving.
These two theories help create structured, effective learning environments—something that every classroom needs.
We shall continue Part 2 of the learning theories in education in our next discussion
Keep following GH Educate for more




very good and helpful